



 (10 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5, rated)
(10 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5, rated)From dial-up modems to the internet of things (IoT), from tortoise like speeds to blazing fast FTTC, from being a static medium to a virtual partner in itself, the rise and adoption of the internet have been nothing short of a revolution. However, it’s just getting started. In the words of Marc Andreessen, the founder of Netscape it is “very, very early on.” As exciting as it may sound, it also raises a few concerns regarding cybersecurity. As a result of their ever-improving skills and resources, cybercriminals have become much more sophisticated with their techniques and approaches. The Comodo Q2 2017 Threat Report is an attempt to understand the very nature of the cyber-attacks we saw in the 2nd quarter of this year.
Comodo Threat Research Labs (CTRL) detects and strategically analyzes the prevalent cybersecurity threats around the world. A group of more than 120 security professionals, ethical hackers, computer scientists, and engineers, who work for Comodo are part of CTRL. The threat report has been derived by detecting threats from 236 country code top-level domains (ccTLD).
To put it in the words of Comodo itself, “This timely study offers strategic insight into the nature of modern cybercrime, cyberespionage, and cyberwar. “
Comodo detected 97 million (M) malware incidents in every corner of the globe. Out of the most prevalent threats facing most enterprises today, Trojans have proved to be most dangerous and most common. The other three breeds of the common malware types are worms, viruses, and backdoors. Here are the numbers:
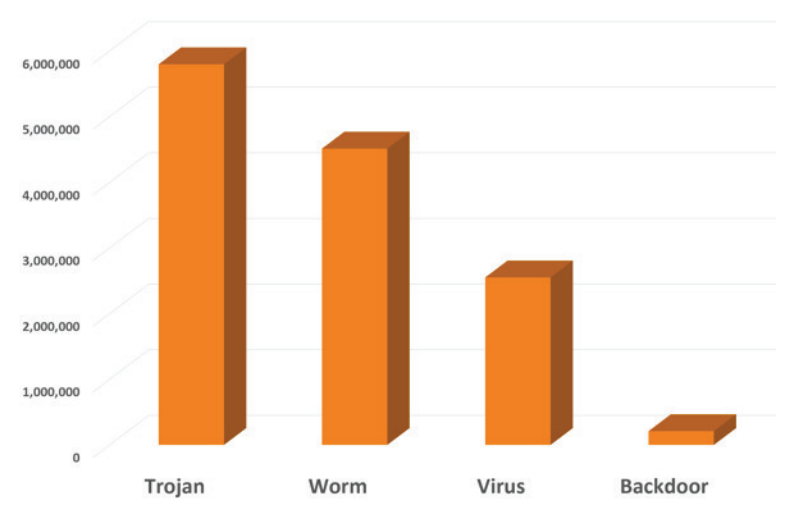
Trojans: 5.8 M incidents
Computer Worms: 4.5 M incidents
Computer Viruses: 2.6 M incidents
Backdoors: 209K incidents
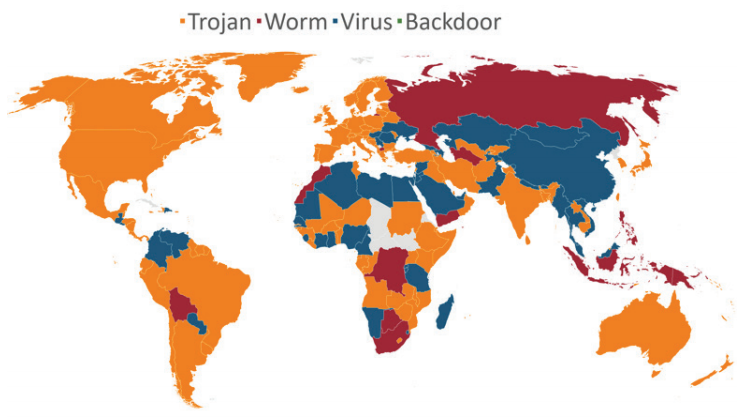
With 1.9 million trojans or over 32% of the total, the US is by far the most trojan-infected country. This is no surprise considering the fact that it ranked the same in Q1 2017 as well. High connectivity and national wealth combine to make the US the most lucrative target for perpetrators.
What if we told you that you can know the economic condition of a country by the type of malware attacks it faces? As bizarre as it sounds, it’s true. It has been found that the higher the “class” of a malware, the more upscale is the country. For example, Backdoors, the highest “class” of malware are seen extensively in affluent countries like Great Britain, Australia, and Japan. On the other hand, viruses tend to be more prevalent in countries with substandard socio-economic conditions.
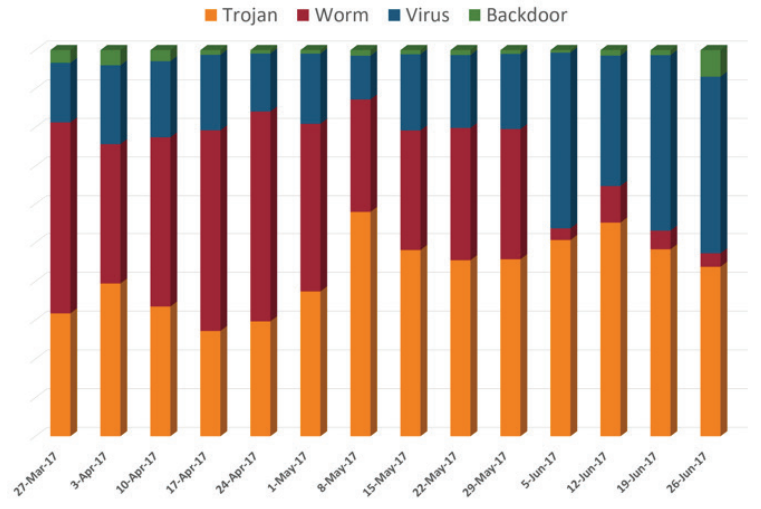
With this report, Comodo has started categorizing malware attacks based on their economic sectors. This provides an interesting insight into the sectors facing the most threats today. With no big surprise, the IT sector leads the way. Online Services, Technology, and Telecom have been the top targets for hackers.
Citing the reason behind this, Comodo’s report states “Attackers are going after information technology (IT) creators and providers in a big way. Why? The reason is becaue, in military parlance, subverting IT is a “force multiplier.” By compromising the software that is used by millions of users around the world, attackers can increase the number and variety of victims to a virtually unlimited number.”
Just like the real world, the world of malware too is dominated by a handful of families. The Upatre trojan family was Comodo’s top trojan detection in Q2. The US, the most trojan-infected country faced 83% of trojan-attacks through Upatre. A similar observation was found in Worms as well. Out of the 4.5M worm detections, almost half of them belonged to the Brontok family. The second most dominating worm family was Autorun.
As far as viruses are concerned, Rammit (49%) and Sality (33%) families grabbed the most attention. DarkKomet (62%), an infamous backdoor malware stole the spotlight. DarkKoment has lived up to its spooky name as we’re still looking for a way to kill it.
One of the main reason behind the meteoritic rise of malware attack has been the social engineering techniques the hackers employ. Using such techniques, the hackers lure the users into clicking on malicious links or downloading files containing malware. Often, they do this by showing a bait to the users. This bait often comes in form of unrealistic offers or discounts. If you see an offer which is too good to be true, it probably is. One of the main reasons behind the proliferation of social engineering techniques is the lack of sophistication it offers. The hackers don’t have to type-in hundreds of lines of codes to infect a system. All they have to do is to send such alluring emails or present such links and the rest is done by the user. This is called ‘phishing’. Therefore, always keep your eyes wide open and don’t get fooled.
More often than not, human mistakes are the prime reason behind all types of cyberattacks. If you have several people working at your workplace, educating them about the do’s and don’ts should be on top of your priority list. You should also insist on using good anti-malware and anti-virus software. Another thing than you absolutely shouldn’t forget is regularly backing up the data of the system. Whether you own a pc or work in an organization or have a server or have a smartphone or have any of other hundred things, BACK UP your data ASAP.