Comodo Code Signing Certificates
Buy or Renew Code Signing Certificate
Add a digital signature to your executables and remove security warnings with a Comodo Code Signing Certificate. When end users download your software, they can be confident your code is secure and has not been tampered with since it was signed.
Code signing certificates and their private keys must be stored on a FIPS-compliant hardware security module or token to protect your digital signature. Want to start signing code quickly? Comodo CA can ship your certificate to you on a FIPS-compliant USB eToken – so you can plug it into your computer and start signing files.
Note: Industry standards require that all code signing certificates be stored on a compliant hardware security module (HSM) or secure USB token. Certificates installed on secure USB tokens cannot be exported; make sure your application supports external hardware if you select this option.
Learn more about certificate delivery options.
Hot
Hot
Hot
Hot
Hot
Hot
Selection Required.
Quantity :
Select US or International Shipping based on your intended shipping address.
- Your Savings:$ 10.00
- Total:$ 208.00
In order to provide you the lowest cost per year, we now offer 2-5 year certificate packages.
To comply with the latest security requirements, you'll need to re-issue the certificate once per year. Don't worry, we'll send you email notifications starting 30 days before it's time to update your certificate! Just follow the instructions in the email to revalidate your domain and reissue the updated certificate.
Have questions? Our customer experience team is available 24/7 to assist you with this process. The 30 day money back guarantee applies to the original purchase date.
Comodo Code Signing Certificate Highlights
- Showcase your verified publisher name
- Ensure software integrity through digital signatures
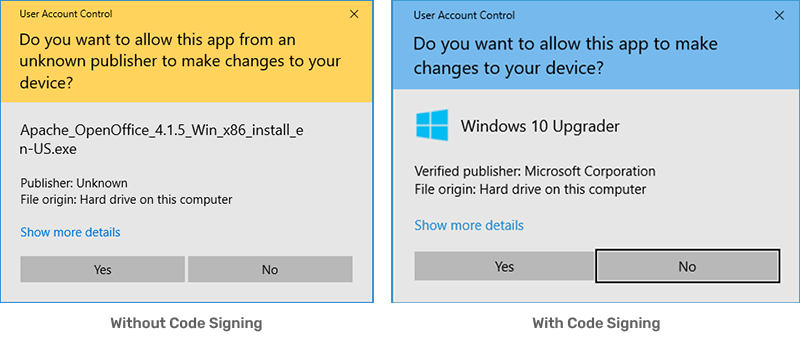
- Remove the “Unknown Publisher” warning
- Typically issued in 4-8 days
- Available to individual developers and registered businesses
- Wide support and compatibility with Windows, Java, and other platforms
- Protect your reputation as a software publisher
- Maintain software authenticity
Comodo Code Signing Certificate Features & Benefits
Boost Customer Confidence
Customers trust software that displays a verified publisher name instead of an “Unknown Publisher” warning. Signed code helps protect end users from malicious code and assures them the code hasn’t been tampered with in transit.
Prove Software Authenticity
When you sign software, you’re proving to users that it’s authentic and published by you, not an imposter. To get a Comodo Code Signing Certificate, the CA must first verify that you are who you say you are. The verification process validates the publisher’s identity, building yet another layer of trust for the end user.
Exceed Industry Standards
All Comodo Code Signing Certificates meet and exceed CA/B Forum and NIST standards and are trusted by popular platforms such as Microsoft Windows. The Comodo Code Signing Certificate uses a 3072-bit public-key and hashing algorithm to generate a secure digital signature.
Secure Private Key Storage
Securely store your private key and certificate in a USB token or hardware security module (HSM). Secure storage ensures your private key and certificate can’t be easily lost or stolen by malicious actors.
Remove Security Warnings
Ensure end users can install and download your software without receiving the Microsoft Windows “Unknown Publisher” warning.
Broad Compatibility
Comodo Code Signing Certificates work with multiple file types, including Mozilla Objects, Microsoft VBA, Adobe AIR, Microsoft Authenticode, Java, and Microsoft Office Macros. Broad compatibility allows you to digitally sign both 32-bit and 64-bit executable files such as .exe, .dll, .csx, .cab, and more.
Support You Can Count On
With every purchase made on ComodoSSLStore.com, you will receive round-the-clock support from our friendly support team. Get 24/7/365 support by phone, email, and chat.
What is Code Signing?
When customers buy software in a store, it's shrink-wrapped and sealed to ensure it hasn’t been tampered with – but what about when they purchase software online?
Code signing certificates serve as a virtual “shrink-wrap” for your software: once you sign your software, any tampering will break the digital signature, warning customers that the code isn’t secure. That way, when customers download digitally signed files (including .exe, .cab, .jar, and more) or drivers from your website, they can be confident your code really comes from you and hasn’t been corrupted since it was signed.
- Assure the software hasn’t been tampered with since it was signed.
- Authenticate the software’s origin from a verified individual or legally registered business.
When Do You Need to Sign Code?
You’ll need to sign your code to distribute the software—whether over the internet, through distributors, or via another medium. When the code is signed, it tells users and customers it hasn’t been altered or tampered with by unknown sources. In addition, signed code helps distinguish legitimate software or code from your organization from fraudulent code from an impersonator.
Aside from verifying the software’s origin and establishing trust with the end user, code signing is essential if you want people to download and install your software or code. People are innately wary of digital downloads and won’t want to download software marked as “unverified” or a potential “security risk.”
Supported Platforms
- Adobe AIR
- Microsoft Authenticode
- Mozilla Objects
- Microsoft Office & VBA
- Java
- Microsoft Windows
Validation Required
Please note: This product requires you to complete Organization and/or Individual Verification, including Telephone Verification and Identity Verification. You must submit a government-issued photo ID for review. Additionally, your organization must be publicly listed on a third-party business directory site (Dun and Bradstreet, Yellow Pages, OpenCorporates, etc.), or you must be prepared to submit a Professional Opinion Letter to verify all required details. Finally, the CA must be able to complete a telephone call with you to complete verification for your certificate. Please review our Organization Validation for Code Signing Knowledgebase article for more information.