



 (24 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5, rated)
(24 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5, rated)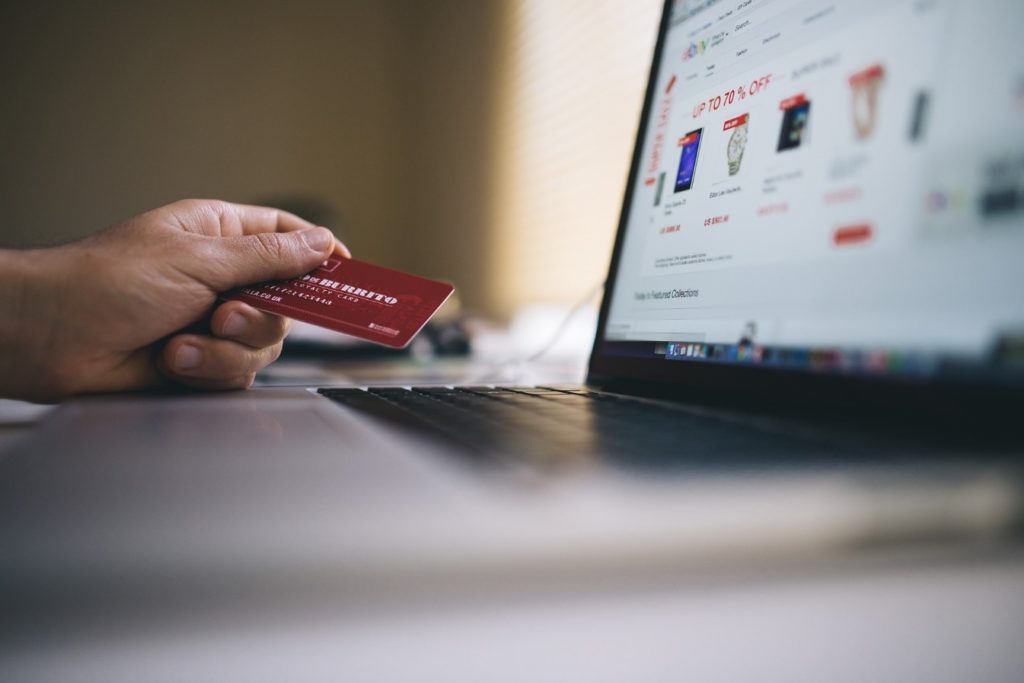
Having an online store has many benefits:
Buyers also love having the ability to explore millions of products at their fingertip and shop while sitting on their comfy couches! Statista reports that e-commerce sales are expected to hit $4.5 trillion in 2021. But when there is something that is loved by the entire world, it gets unwanted attention, too. According to the Annual Cybercrime Report (ACR) from Cybersecurity Ventures, Cybercrime damages are estimated to cost businesses $6 trillion annually by 2021.
Yes, cybercrime in the eCommerce industry is the elephant in the room, and it’s the high time we talk about it. Protecting your website from cyberattacks is crucial for any eCommerce business’s survival, irrespective of the size of the organization.
In this article, we’ll cover the 10 most essential tips to protect your eCommerce website:
It’s tempting to choose the cheapest hosting plan available in the market when you are facing tight budgetary constraints. Many business owners have the misconception that all hosting sites are equal. Unfortunately, that impression is far from the truth. Factors such as website security, speed, SEO, and the site’s traffic-handling capacity are heavily dependent upon your hosting environment.
When you select a hosting plan, make sure you investigate what security measures they implement to protect their clients’ websites. Are they providing up-to-date server software, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack protection, hack protection, automatic backups, daily malware scan, spam protection, and email protection?
If you’re not sure about their security tools, contact their customer support and ask them about it. Some web hosts will offer you security features for an extra fee, as a top-up to your main hosting plan. Consider all those additional security costs when comparing hosting plans.
In addition, cloud-based DNS hosting services and managed DNS services are cost-efficient solutions to protect your site against DDoS attacks.
One of the most common sources of security breaches is outdated software. Fortunately, there’s a simple fix.
If you’re using WordPress for your eCommerce store, update all components such as WordPress software, plugins, themes, etc., as soon as an update is available. If it’s not a WordPress site, you’ll still have to keep an eye on updates. Whether it’s a web server or third-party code like Java, Python, Perl, WordPress, and Joomla — whenever the new version is released, immediately install it on your system.
Updates are released for a good reason. A manufacturer’s software team often releases the updated version after fixing the vulnerability of the previous versions. If you don’t upgrade, hackers can easily exploit the security vulnerabilities of the old technology.
A correctly configured firewall is a critical part of your website security strategy – it can give you a strong defense against attacks such as distributed denial of service (DDoS), SQL injection, and cross-site request forgery. Firewalls continuously monitor and immediately block any suspicious traffic or requests (before they reach your website). Best of all, website firewall plugins and software are available inexpensively for small businesses.
Most eCommerce websites make their users create an account to complete the checkout process. It’s a good practice for tracking customers’ buying behaviors and developing future marketing strategies, as well as making future purchases faster for the customer. If many users have accounts on your website — employees, vendors, distributors, authors, co-admins, etc. — and any of them uses a weak password, their account becomes an easy target for a brute force attack.
An easy password can make your website vulnerable and easy for hackers to get into. That’s why you should require your users to use strong passwords. If your website uses WordPress, you can use a plugin like Force Strong Passwords to enforce strong passwords. If it’s not a WordPress website, ask your developers to set conditions in the code to accept a password only if it contains a minimum number of characters, an uppercase letter, a lowercase letter, a number, and a special character.
Plus, people have a tendency to use the same passwords for multiple accounts. So, if the hacker gets access to your customers’ password, they can access the customers’ accounts on other websites as well.
Most financial institutes offer their users two-factor verification or two-factor authentication (2FA). When making any financial transactions, users have to pass through an additional layer of security along with their traditional passwords. The most popular two-factor authorization method is sending a security code or one-time password (OTP) to a user’s cell phone. The user then needs to provide this verification code to proceed further with their transaction.
You can also enable two-factor authentication on your online store. If you’re using a WordPress site, you can enable 2FA with the Google Authenticator plugin.
Obtaining and maintaining Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance is vital for every business that accepts credit/debit card payments, regardless of its size. The PCI self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) guidebook has a list of various requirements that you must meet to achieve PCI accreditation and can help you to identify any loopholes in your company’s payment security.
Make any necessary changes in your payment security to meet the guidelines and complete a PCI compliance scan using a tool like Comodo HackerGuardian. Once you get the report, submit the SAQ, scan report, and other required documents to your bank. If everything meets their requirements, your company will be PCI DSS compliant.
Installing an SSL certificate is an essential part of PCI compliance. A Comodo SSL certificate achieves the following:

Some eCommerce websites want to collect as much customer information as possible to analyze consumer behavior and demographics to make efficient marketing decisions. Some online stores also enable customers to save their credit/debit card numbers, CVV codes and other related data to their accounts to provide a user-friendly customer experience during the checkout process.
Though convenient for users, unfortunately, saving confidential customer data on your own server is highly risky. If a hacker cracks your system and gains access to your users’ information, your company may have to pay a massive penalty for the data leak or data breach. Only big eCommerce players that have in-house cybersecurity teams constantly working on protecting the website can afford to take such risks. For small/new eCommerce sites, the risk of data leakage outweighs the benefit of saving customers data.
Fortunately, there’s an easy solution – use a third-party payment gateway such as PayPal, Stripe, Skrill, etc. to facilitate online payments to reduce your risk. These providers can enable saving payment details without saving the details to your server.
No matter how secure your website is, you still need to have a working and tested disaster recovery plan (DRP) in place. Part of this plan includes making sure your hosting company automates data backups. You should also perform regular backups on your end as well.
It’s not only hacking incidents but also viruses, human error, system failures, or natural disasters that put your data at risk. So always maintain current backups in multiple geographic locations.
Tip: CodeGuard automatically backs up your website daily, encrypting and saving your data on AWS servers. You’ll always have a copy of your website to fall back to if something breaks!
Educate your employees on data protection policies such as not sharing customers’ sensitive data in chat or email and how to avoid phishing attacks. You should conduct regular security training sessions to ensure they are aware and informed of your organization’s security rules and regulations, key cyber security best practices, and know how to identify and respond to online threats so they don’t click on or open anything suspicious from your company’s devices. You should make a written copy of the company’s data protection policies, too.
If you are wondering, “are these 10 steps enough to protect my eCommerce website?” Well, nothing is ever enough in the cyber security industry. Maintaining a strong cyber security posture for your eCommerce website is an ongoing process, and you need to keep updating your technology and processes every day. But, yes, these are the foundational steps of website security, and you can avoid many prevalent widely used cyberattacks by implementing these. If you skip any of the above 10 security tips, you’re leaving your website vulnerable and hacker friendly.