How to Fix a “404 Page Not Found” Error in WordPress

A negative online experience deters about 73% of users from returning to a website. To improve retention, website owners should focus on resolving issues like “404 page not found” errors, which disrupt user engagement and deter repeat visits.
On the digital landscape, a website is typically the first interaction that a business has with its potential customers.
As the adage goes, first impressions are crucial. And that’s why having a website that’s error free, aesthetically pleasing, and easy-to-navigate is paramount.
This article sheds light on a common issue that WordPress website owners often encounter: the dreaded “404 page not found” error in WordPress. We’ll walk you through how to fix this error, which results in a page not being displayed to site users.
What Is a “404 Not Found” Error in WordPress?
A 404 error is a browser hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) error code that communicates that a particular file (i.e., a website page) can’t be located by the server. They’re often called dead or broken links because, as the name implies, they don’t lead anywhere (much like a dead-end street).
Have you ever clicked on a link or typed in a URL only to be met with a message that says “404 page not found?” This error occurs when the server hosting the website can’t locate the specific page or resource you are trying to access. It’s like trying to find a book in a library, but the librarian can’t locate it on the shelves.
This is what it looks like when you trigger a 404 error on ComodoSSLstore.com’s WordPress website:
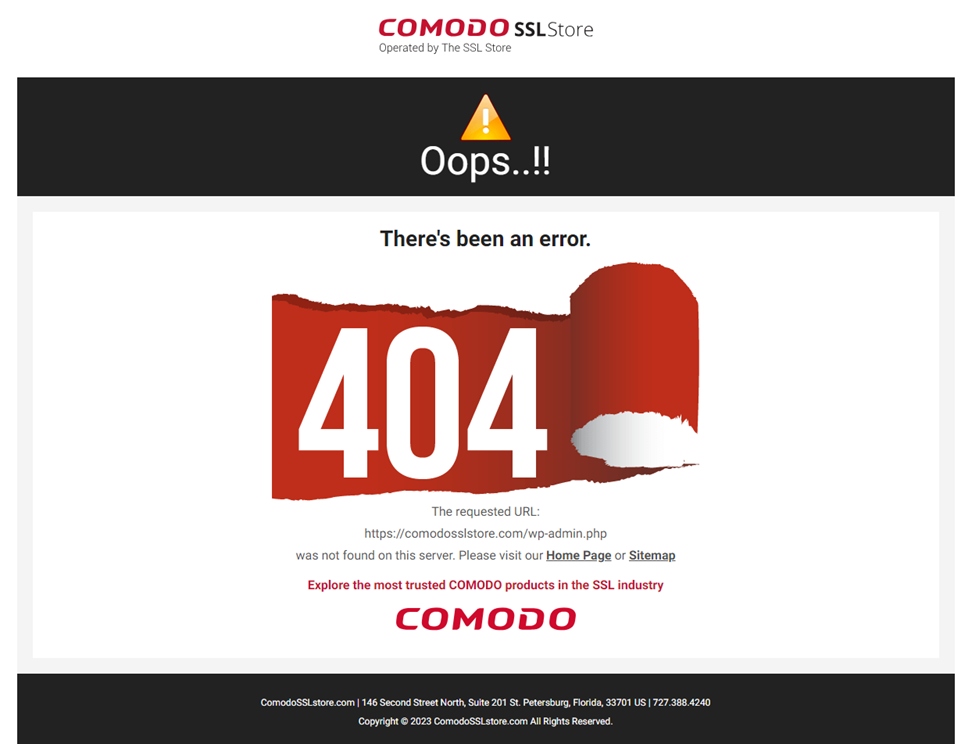
While frustrating as a user, it’s important to remember that this error is not a problem with your device or internet connection. Rather, it’s a client-side issue that’s triggered by an issue on the server. It occurs when the website’s server can’t find the file or URL you’re requesting, resulting in the browser displaying the error in response to your page query.
What Do HTTP Status Codes Like Error 404 Signal?
A 404 is an HTTP status code that communicates a page is unavailable for an undisclosed period. (The web page could be down for a few minutes or the page many be gone permanently — you don’t know; you just know it’s missing at the moment.) Now, website status codes act as messengers to talk to your visitors to communicate specific information. These codes are categorized into 1xx and 5xx ranges, each representing a different type of server response.
Also, status codes help your website’s server communicate with their web browsers. Think of these codes as different signals sent in different situations.
Let’s focus on one specific code. When a site visitor tries to open one of your web pages, their browser expects a response from your server. So, a friendly 200 code is sent to the browser if the page exists, and all is well. But if a page they’ve requested is nowhere to be found, a less-friendly 400-range code appears, like the 404 error example we showed a little earlier. This HTTP code lets all site visitors know the requested page couldn’t be found.
What Causes the “404 Page Not Found” Error?
If you’re a website owner or developer, discovering 404 errors on your site can be frustrating and confusing. To a certain point, however, 404 errors are unavoidable because you can’t stop Google or other search engines from trying to crawl URLs that no longer exist.
Let’s first discuss the common causes of 404 errors and specific scenarios that can lead to them.
Common 404 Error Causes
- DNS settings issue: If your website’s DNS settings are not configured correctly, it can lead to 404 errors. This problem can arise due to the domain name system (DNS) pointing to the wrong IP address. In such cases, browsers might not be able to find your site’s server, resulting in a 404 error.
- Caching problems: Caching problems can cause persistent 404 errors, even when the website is functional for others. From a user perspective, this issue occurs when the browser caches the 404 error page instead of the actual content. Similarly, server-side caching can also lead to 404 errors if the cache hasn’t been updated after a page has been moved or deleted.
- Directory issues: Sometimes, the issue is with the folder containing the page (directory) rather than the page itself. When a folder containing pages is moved, the URL for each page within it changes, leading to 404 errors if not updated to reflect the change.
- Missing asset: Missing assets like images, CSS, or JavaScript files on a page can also generate 404 errors, as the server cannot find these resources.
- URL problems
- Shifting a page or directory: Moving a page or its directory to a new URL without updating the links that point to it can cause a 404 error. This includes shifting a page’s directory or moving the entire website, which changes the URL structure. For example, changing a page’s directory from https://codesigningstore.com/new-directory/random-page to https://codesigningstore.com/new-directory/random-page could result in a 404 error.”
- Failing to redirect: If a page or resource is relocated and the old URL is not redirected to the new one, this results in a 404 error. Also, if you’ve set up a redirect, but it’s configured incorrectly, users will be led to a non-existent page.
- Missed 301 redirects: Not using 301 redirects when moving pages or the entire site can cause 404 errors. A 301 redirect is essential to inform both users and search engines about the permanent relocation of a page to a new URL.
- Spelling errors in URLs: Simple typos in URLs can also lead to 404 errors. Providing the correct spelling of URLs is a basic but often overlooked aspect.
- Mistyped URL: Entering the wrong URL into the browser’s address bar can lead to a 404 error. This can be due to incorrect linking or typographical errors when writing the URL.
Specific Scenarios:
For instance, a visitor, upon landing on your website, may encounter a 404 error if you have done one of the following:
- made changes to the URL or,
- hidden the URL for editing purposes.
Again, have you ever published a post with a lengthy URL only to shorten it later? If someone tries to access the old URL, they will be directed to a 404 error page. If you try to use a link shortening service (e.g., bit.ly), if the original URL is removed, the shortened URL will typically result in a “404 page not found” error.
Don’t let a non-existent or mistyped URL ruin your visitor’s experience. Create a custom 404 error page to guide them back on track.
The Impact of 404 Errors on Your WordPress Site’s Search Rankings, User Experience, and Brand Reputation
A PricewaterhouseCoopers (PWC) report uncovered that 32% of loyal customers would abandon their favorite brand after just one negative experience. This nearly one-in-three statistic underscores the critical role of a safe and user-friendly website in retaining brand loyalty.
On the face of it, 404 errors can undoubtedly harm your website’s SEO and rankings.
404 Errors Aren’t SEO Friendly
Search engines dislike encountering HTTP status code errors as they indicate an issue with the web page. When left unresolved, 404 errors obstruct search engine crawlers from accessing your site’s content. This happens because crawlers often follow internal links within your website.
A 404 error page causes search engines to assume the page lacks content, negatively impacting your search engine optimization efforts.
404 Errors Aren’t Buyer Friendly
Also, a 404 error on eCommerce sites deprives potential buyers of a smooth and enjoyable buying experience. When errors occur frequently, shoppers will likely leave your site and may not return, preventing you from converting them into customers.
404 Errors Aren’t Visitor Friendly
When other visitors encounter a 404 error, it disrupts their anticipated smooth navigation, leading to a negative experience. This occurs as users expect to access the desired content directly through links. Such errors not only result in a disappointing user experience but also reduce website traffic and hinder the site’s ability to gain link equity, which is essential for search engine rankings.
The repercussions of 404 errors are multifaceted, affecting user satisfaction, business outcomes, and brand perception.
They Can Negatively Effect on Your Brand’s Reputation
Regular occurrences of 404 errors can adversely affect your brand’s image. A reliable and functional online presence is crucial for fostering consumer trust. Frequent 404 errors, suggesting technical shortcomings or site maintenance-related issues that can diminish user trust and negatively impact your brand’s credibility.
These Errors Can Adversely Impact Your Conversions and Business Relationships
Frequent 404 errors can significantly undermine a website’s ability to engage and convert visitors into customers. These interruptions often result in immediate sales losses and can damage long-term customer relationships.
Addressing 404 errors is not just about fixing broken links: it’s about securing a positive, uninterrupted experience for every visitor. This, in turn, strengthens your brand’s online presence and supports its success.
How to Fix a “404 Page Not Found” Error in WordPress
404 page errors are common on WordPress websites and can be caused by various factors, such as hosting conflicts or changing URL slugs.
Dealing with these errors can be distressing for beginning web developers, but it’s important to remember that everyone experiences them at some point. The following points will further discuss the technical methods to resolve fix a “404 not found” error in WordPress.
1. Update WordPress Permalinks
If you’re encountering 404 errors throughout the website while attempting to access content, the root cause is most likely linked to problems with your permalinks.
Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual blog posts, as well as categories and other lists of blog postings. They are used to ensure that your content remains accessible under the same address over time, which is essential for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO). If these links are broken or incorrect, they can lead to 404 errors.
Alternatively, the issue could be with your .htaccess file if your host uses Apache. This file is responsible for important settings that control how your server responds to requests, including URL redirections and rewrites. A misconfiguration here can prevent access to content and result in 404 errors.
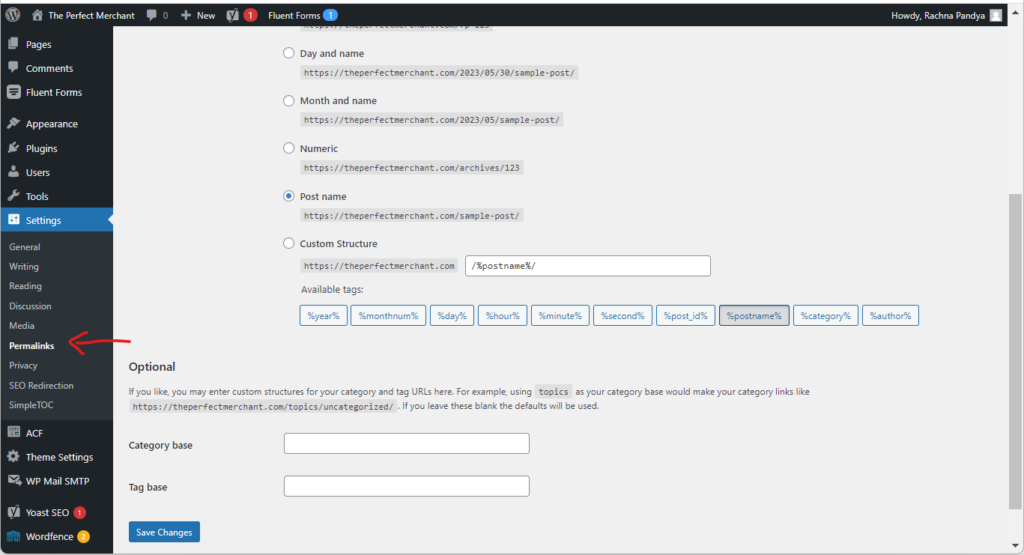
To fix a permalink-related “404 page not found” error in WordPress:
- You will need to go to your permalinks menu in WordPress, which can be found in the settings section. Choose the Permalinks option and save changes.
- Again, no changes are necessary; simply clicking the Save Changes button will suffice.
- If the 404 issue persists even after saving the permalinks, manually reset your existing permalinks by editing the .htaccess file using FTPS or SSH.
- This is especially helpful when meeting error 404 messages after migrating from one domain to another.
Likewise, updating permalinks and clearing your website’s cache can often solve URL-related problems within WordPress.
2. Configure 301 Redirects
While moving or renaming content on your website, setting up a 301 redirect is a wise move.
There are several reasons why you should set up a 301 redirect:
- Provides a seamless transition: Users are automatically directed to the new location for a smooth browsing experience.
- Retains SEO value: This approach helps you maintain domain authority from backlinks and preserve search engine rankings.
- Avoids 404 errors: Not displaying these disruptive errors prevents frustrating dead ends for site visitors.
You can use redirect plugins with user-friendly interfaces or set up manual 301 redirects using the .htaccess file to make it easier.
3. Utilize Google Insights
Google offers tools that can assist website owners in identifying and troubleshooting 404 errors identified by its crawlers.
Why Use Search Console?
- It is recognized for its straightforward and practical approach.
- Google Console utilizes Google’s existing site crawling, which can be more efficient than third-party plugins or additional site scans.
Why Analytics?
- Google Analytics facilitates the monitoring and analysis of 404 errors through its reporting features.
- Reports from Google can pinpoint broken links, both internally and externally, which may be causing issues on your site.
Employing Google’s tools to gather insights can be a strategic part of analyzing and improving website performance.
Other Ways to Resolve Common 404 Error Causes
- DNS settings issue: Confirm your DNS settings are correct and fully propagated to avoid 404 errors related to domain resolution.
- Caching problems: Regularly clear your site’s cache and ensure browser cache settings are properly configured to prevent outdated pages from causing errors.
- Directory issues: When moving a directory, update the URLs for each contained page to reflect the new paths and prevent 404 errors.
- Missing asset: Verify all page assets, such as images and scripts, are present and correctly linked to ensure they are accessible to users and search engines.
- URL problems:
- Shifting a page or directory: Adjust your internal links to reflect any changes in page locations or directory structures.
- Failing to redirect: Set up proper redirection for relocated resources to maintain accessibility.
- Missed 301 redirects: Implement 301 redirects when pages are moved to inform both users and search engines of the new location.
- Spelling errors in URLs: Double-check and correct any typographical errors in URLs to eliminate broken links.
- Mistyped URLs: Educate users on using correct URLs and provide clear navigation aids to minimize input errors.
Final Thoughts on Dealing with the WordPress “404 Not Found” Issue
On a final note, 404 errors are inevitable on your website, especially as your website grows in size over time. To effectively address this issue, establish a workflow to monitor and resolve WordPress errors periodically. This can be done using a combination of manual and automated methods.
Google’s method for indexing and ranking sites considers these errors, underscoring the importance of diligent 404 error management. Frequent 404 errors may signal to users and search engines that a website lacks current updates or proper upkeep, potentially deterring visits and affecting search rankings. Timely rectifying these errors is essential to present a well-maintained site and retain visitor confidence in your site’s dependability.
If this has helped you or you have added clarifications, please get in touch with our web guard experts to help you resolve these and other WordPress website errors on your site.


