Comodo Q2 2018 Threat Report: Key Takeaways
Looking at the cybersecurity trends from April-June of 2018
Comodo Threat Research Labs (CTRL) conducts thorough research and analysis of the cybersecurity threats that continue to plague us online. The research team consists of over 120 security professions and computer scientists who study all prevalent cyber threats to develop strategies and insights on how to keep our online environment safe.
In this article, we’ll present an abridged version of their findings as compiled in the Comodo Cybersecurity Global Threat Report for the 2nd Quarter of 2018.
Key Takeaways from an analysis of 400 million malware incidents detected in Q2, 2018
Geographical Overview
In the second quarter of 2018, 400 million unique samples of malware were detected across the top-level domains of 237 countries. The following are a few takeaways.
Countries with the highest number of worm infections: Russia, Turkey, and India.
Russia, Turkey, and India were the countries with the highest worm infections in Q2, 2018. The sharpest infestations occurred in Turkey and India in mid-April and mid-May respectively.
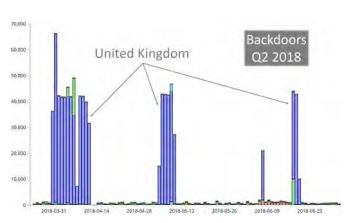
Country with the highest proportion of detected backdoors: United Kingdom.
The most common backdoor detected by Comodo was Dark Komet, a backdoor used for cyber espionage. The United Kingdom was the most significant victim of this malware in 2018.
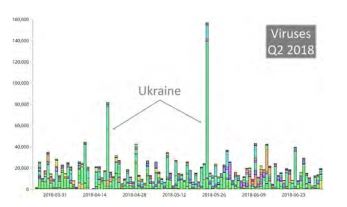
Countries with the highest number of detected viruses: Ukraine and Russia.
Ukraine, Russia, and other developing countries were most affected by viruses. Ukraine experienced two significant infestations in mid-April and mid-May 2018.
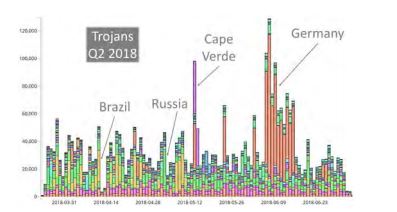
Country with the greatest Trojan threat: Germany.
Germany is the #1 Trojan-targeted country in the world and it experienced a massive Trojan infestation in the beginning of June 2018.
Trojans remain a major threat
In 2017, Trojans had been the most pernicious and prevalent malware threat, with 5.8 million confirmed Trojan incidents. In 2018, Trojans have merged with phishing emails to further amplify their spread, thus becoming an even more prevalent form of malware.
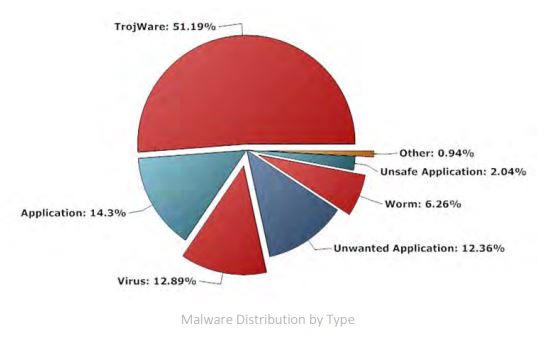
The following numbers illustrate the percentage to which the Trojan threat dominates the cybersecurity landscape:
- Trojware: 51.19%
- Applications: 14.3%
- Virus: 12.89%
- Unwanted Applications: 12.36%
- Worms: 6.26%
- Unsafe Applications: 2.04%
- Others: 0.94%
As you can see, TrojWare is currently the greatest threat to cybersecurity.
New threat posed by Cryptominers
Cryptominers don’t yet represent a significant threat in terms of volume. Furthermore, in 2018, crypto mining activity has decreased since last year. However, cryptominers still pose a new and burgeoning form of threat that must be dealt with in its infancy.
In the past, cryptominers used infected machine resources to mine cryptocurrency for the hacker, thus merely sucking up CPU resources and little more. However, recently, cryptominers have become more sophisticated and they can hide and fight against anti-malware tools and crash user systems.
Cryptominer-driven malware and cyberthreats are spreading to the whole world, most notably to North America, Russia, and parts of Europe and Asia.
Android phones are highly susceptible
CTRL detected a major spike in malware targeted towards Android phones because they carry a treasure trove of personal, corporate, and even government data. Some of the most commonly detected forms of Android malware were KevDroid, Zoo Park, MikeSpy, Xloader, Stalker Spy, Mystery Bot, FakeSpy, RedAlert, Hero Rat, Sonvpay, and CoinHive.
Below is a detailed overview of Android-targeted malware during the months of April, May, and June 2018.
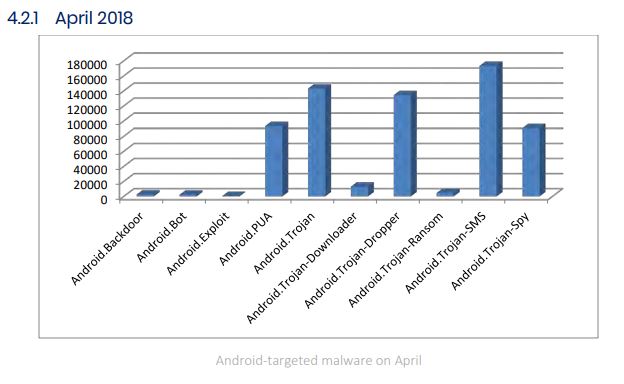
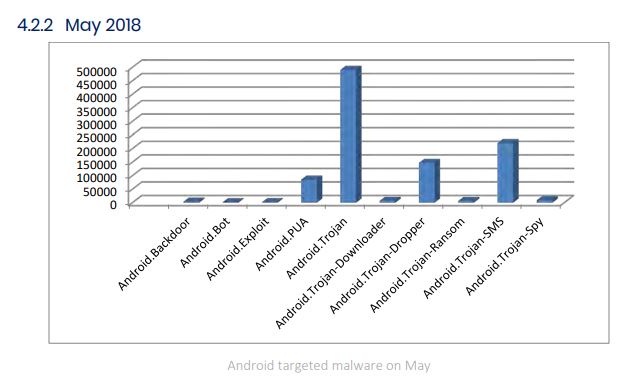
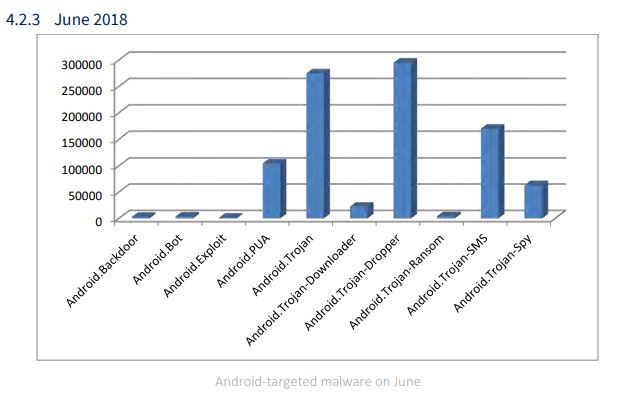
Kryptik and Zbot stand as the most prevalent malware families
Comodo Threat Research Labs also identified the most prevalent threats across 22 vertical markets or industries such as Automotive, Healthcare, Retail, etc. It covered four malware types — Backdoors, Trojans, Viruses, and Worms.
The study determined that two Trojans — Kryptik and Zbot — were the most prevalent forms of malware across most verticals.
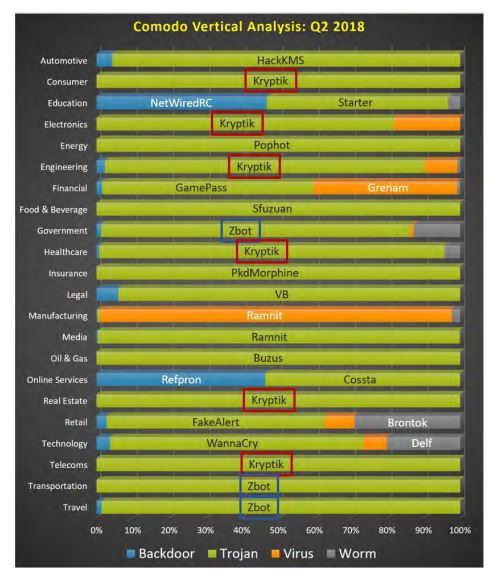
Kryptik had initially been created to obtain information about an infected host’s FTP servers. However, it has now evolved and has the ability to target email clients, file browsers, and file managers. It has largely spread through the downloads of Microsoft Silverlight and Adobe Flash.
Zbot, short for Zeus Trojan, has been targeting and undermining Microsoft Windows security since it was first detected in 2007. It’s largely used to target governmental organizations and the transportation industry. It can also be used to steal financial information like account number, passcode, keylogging, etc.
Key Points
- Comodo detected 400 million malware incidents across the globe in the second quarter of 2018.
- Trojans continue to be the biggest threat to cybersecurity, taking up 51.19% of all the malware.
- Kryptik and Zbot are the most prevalent malware families.
- Germany was the most highly targeted country amongst Trojans.
- Russia, Turkey, and India were the countries with the highest worm infections.
- Ukraine, Russia, and other developing countries were most affected by viruses.
- The United Kingdom was the most significant victim of backdoors.
- Cryptominers are growing into a potentially serious cybersecurity threat.
- Android devices are the prime target of hackers.
Cybersecurity threats continue increasing at an alarming pace. In the second quarter of 2017, Comodo had detected 97 million malware incidents. That number has shot up to 400 million in the second quarter of 2018. One of the key findings of the report is that Android devices are currently the prime target of hackers because they contain a host of information about governments, individuals, and corporations. In order to prevent yourself (or your employees) from being susceptible to hacks and malware, you need to use good anti-malware and anti-virus software and also educate yourself and your employees about the dos and don’ts of internet security.


 (21 votes, average: 4.24 out of 5)
(21 votes, average: 4.24 out of 5)