What is SSL Stripping? A Beginner’s Guide to SSL Strip Attacks
Understand the con trick that is SSL Stripping or HTTP Downgrade
SSL Stripping or an SSL Downgrade Attack is an attack used to circumvent the security enforced by SSL certificates on HTTPS-enabled websites. In other words, SSL stripping is a technique that downgrades your connection from secure HTTPS to insecure HTTP and exposes you to eavesdropping and data manipulation. Think of it as wiretapping, but a bit more technical. When your web browser comes into contact with a web server, the first contact is made using ordinary TCP and then the user is redirected to TLS/SSL. Hackers take advantage of this small window using SSL strip or SSL downgrade attacks.
Moxie Marlinspike, American computer security researcher and cypher punk first demonstrated how one can bypass HTTPS security. It is a very dangerous technique that could prompt huge implications from a user’s point of view. Let’s see how it works.
SSL Stripping: A con trick
Fundamentally, SSL strip attacks function the same way as a con trick does. In SSL Stripping, a user is made to believe that the connection is secure and the data he/she sends is encrypted. But in reality, the connection is insecure and data is sent in plain text, stripping off the encryption. That’s why the name SSL ‘strip’.
To execute an SSL strip attack, there must be three entities – victim’s system, secure web server, and attacker’s system. Had there been no attacker in between, the communication would only happen between victim’s system and the web server of website. An SSL stripping attack is employed to kill this secure communication without making the victim realize. The Attacker/hacker uses a proxy server and his/her coding skills to pull off this trick.
Let’s see how it’s done with an example.
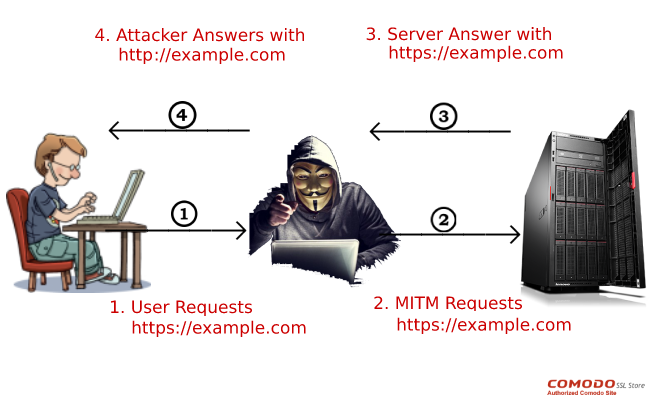
Suppose Nick wants to send some money by accessing a secure, HTTPS-enabled website. But Bob, who is a hacker, wants to intercept this communication and see Nick’s credentials. To accomplish this, he establishes a connection with the victim, thereby cutting Nick’s communication with the secure server. When Nick requests to visit the banking site on his browser, Bob gets it and forwards it to the server of the banking site. A thing to note here is that all the communication taking place between Bob and the website is SSL protected.
The web server responds to Bob’s (originally Nick’s) request in form of an HTTPS URL. Now using his precarious and delicate coding skills, Bob downgrades this secure HTTPS URL to insecure HTTP URL and forwards it to Nick. The beauty (or fatality!) of the attack is such that poor Nick can’t have any clue what’s happening in the background. As the connection is over stripped HTTP protocol, everything Nick sends would be in plain text only. His passwords, banking details, credit card details…everything he sends to this URL can be seen by Bob. As the connection is downgraded from HTTPS to HTTP, stripping attacks are also known as HTTP Downgrade attacks.
Primarily, there are three ways through which SSL stripping attacks can be executed. They are:
- Using Proxy Server
- ARP Spoofing
- Using Hotspot
How to protect my website against SSL Strip attacks?
SSL or HTTPS is an idea, a wonderful idea indeed. Just like any other idea out there, there are loopholes in it. And such loopholes must be addressed. Here are the three things you can do to make your HTTPS website even more secure:
- Enable HTTPS on pages of your website
- Implement HSTS policy – A Strict policy under which browser won’t open a page unless the site has HTTPS.
Save Up to 75% On
Comodo SSL Certificates
Tip: You can typically save a significant amount by buying your SSL certificate direct instead of through your web hosting company. We sell all Comodo SSL certificates at up to 75% off.


 (16 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
(16 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)