What is SSL? How do SSL Certificates work?
The Complete Beginner’s Guide to SSL Certificates & Encryption
‘What is an SSL Certificate?’—this is one of the most cliché questions on the Internet. Cliché but useful nonetheless. Technically, SSL/TLS can be defined as a ‘cryptographic protocol’ that provides secure communication between a web browser and a server.
SSL stands for ‘Secure Socket Layer’. It is also known as TLS, short for ‘Transfer Layer Security’. SSL certificates are widely used in websites, mobile apps, emails, fax, messaging, etc. Generally, an SSL certificate is deployed on a website—its most common usage. While browsing on the internet, you may have noticed that some sites say HTTPS while some say HTTP. You may have wondered what’s the difference between the two. Well, an SSL certificate is the difference here.
The ‘S’ in HTTPS stands for security. An SSL certificate secures the communication between your PC/Cellphone and the web server of an HTTPS-enabled website.
Why SSL?
When you access a website, communication takes place between the web browser of your PC/Mobile and the web server of the website. Information/data is transferred from both sides. An SSL certificate protects the information transferred between both. This is compelling from a security and privacy point of view. Every day, we all send confidential information across the internet in abundance. This includes delicate information such as email IDs, user IDs, passwords, credit/debit card details, bank account details, etc. If such confidential data is transmitted over an unprotected protocol, there is a significant risk of such private information coming in the hands of cyber criminals. Such interception of data being transmitted is called a Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack.
As far as organizations are concerned, the importance of data security should be taken even more seriously. In any organization, a colossal amount of secret data is transferred, whether it is inside the organization or outside. If even a single document is leaked, it can cause a considerable amount of damage to the organization. This is where SSL certificates enter the picture.
What does an SSL certificate do?
We all have sent/received something in an envelope, right? You must have used (or at least seen!) an envelope seal to keep the documents safe. Simply put, that is what an SSL certificate does. An SSL certificate safeguards any information being transferred between a client and a server. This is done via Encryption.
What is encryption?
As stated above, SSL certificates facilitate Encryption. Let’s talk about how that works. If you send any data on an HTTPS-enabled website, that piece of information is converted into an unreadable string of characters. For example, if your password is 1234, then it might be converted into something like ^%jrt5/*u. This makes it virtually impossible for any hacker to interpret the information, even if he/she manages to intercept the data somehow.
This Encryption technique has been used for centuries. It is believed that Julius Caesar was the first person to use it. It is referred as Caesar’s Cipher. Compared to Caesar’s Cipher, today’s encryption methods are much more complex. Specific algorithms are applied to change the bundle of data into an undecipherable format. Forget about humans, these algorithms are so complex in nature that even supercomputers can’t crack them. Seriously, it would take a supercomputer over 100 years to crack 256-bit encryption.
How do SSL certificates work?
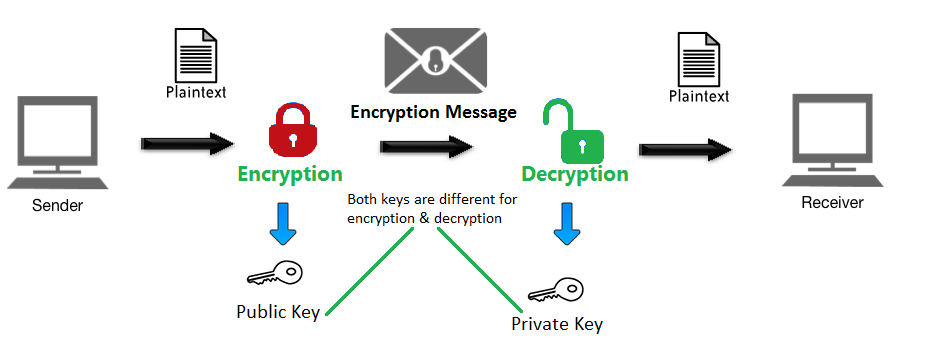
SSL certificates work based on public key infrastructure (PKI) or public key cryptography. This method involves two distinct cryptographic keys—Private Key and Public Key. The public key is used for encryption purposes and the private key is for decryption.
As the name implies, the Public Key is shared with everyone who receives the certificate upon visiting a website. You are using the public key without even knowing it. These keys are stored in the digital certificate. You can see the public key of a website by viewing the SSL certificate details in your browser.
Both the keys are different but related to each other. This means that the information encrypted using a particular public key can only be decrypted using the private key attached to it. A secure connection is established if the client can verify that the public key matches the private key. This is called ‘Asymmetric Encryption’.
The SSL Handshake
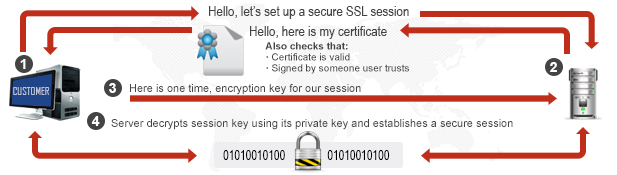
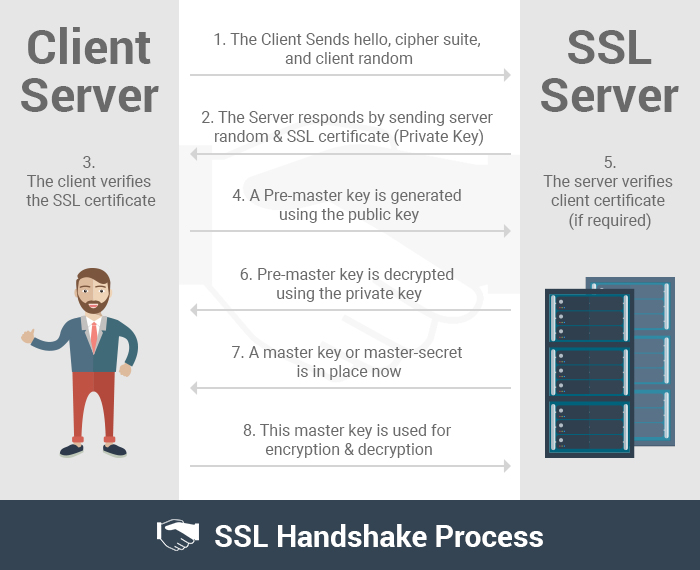
The process of establishing a secure connection is referred as an ‘SSL handshake.’ It’s not like the old-fashioned handshake that we all do every day. Instead, it’s a modern-day version of a handshake (just like the “cool” millennials do). This handshake involves three steps (no dabbing involved!)—hello, server verification, and transfer of keys.
- Hello: As we (well, most of us!) all do upon meeting someone, the client and the server say Hello to each other. The client sends a ClientHello message to the server. This “Hello” contains some SSL certificate information. In response to this ClientHello message, the server responds to it by ServerHello message. Likewise, it also consists of similar information as the ClientHello message.
- Server Verification: Now a secure connection is in place between the client and the server (a good amount of comfort between the two!). Now, this is the stage where the client verifies the identity of the server. How exactly? Through an SSL certificate. An SSL certificate contains information of the owner/organization, its location public key, validity dates etc. The client makes sure that a valid certificate authority (CA) has validated the certificate.
- Transfer of Keys: Once the client verifies & authenticates the server, it’s time for both the parties to share their keys. After the verification of the server is done, the client uses the public key to generate a pre-master key. Then this pre-master key is sent to the server. The server decrypts this pre-master key using its private key. This way a new key is computed by the client and the server. This is an example of Asymmetric Encryption. This master key is used to encrypt and decrypt the information transferred between the client and the server. This is called Symmetric Encryption. Thus, both the techniques of Encryption are deployed to ensure a secure connection.
What details does an SSL certificate include?
An SSL certificate includes the details of the party to whom the certificate has been issued. It includes the following information:
- Domain Name
- Certificate Validity Period
- Certificate Authority (CA) Details
- Public Key
- Public Key Algorithm
- Certificate Signature Algorithm
- SSL/TLS Version
- Thumbprint
- Thumbprint Algorithm
The aforementioned information is included no matter which type of SSL certificate has been installed on the website. However, some additional information is also provided in the advanced level SSL certificates. For instance, organization validation (OV) and extended validation (EV) SSL certificates include details of the organization such as:
- Name of the organization
- Website owner
- Address
- City
- State
- Country
- etc.
Click here to learn about different types of SSL certificates.
How to identify an SSL-enabled website?
By now, you understand the ins and outs of SSL certificates and encryption. But you might be wondering how you can tell if a site has installed SSL or not. Well, there is a fine line between an SSL-enabled website and a non-SSL website. However, many fail to spot it. Let us help you. An SSL-enabled website comes with special indicators that set them apart from the other websites. Green address bar, padlock, site-seal etc. are examples of such indicators—trust-signs if you call it.

Last Word
The number of data breaches and their magnitude keeps touching new horizons with each passing day. As a result, SSL certificates have become a prerequisite for any platforms dealing with sensitive information. Aside from data-security, SSL certificates can help in many ways. This includes better search engine ranking, enhanced reputation, improved customer trust, high conversion rates, greater revenues etc.
Combining the benefits and needs of the SSL certificates, it’s safe to say that ‘Encryption is coming’.
What is a SAN Certificate? Information About SAN SSL Certificate

 (21 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)
(21 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)