Rate this article: 


 (16 votes, average: 2.94)
(16 votes, average: 2.94)



 (16 votes, average: 2.94)
(16 votes, average: 2.94)Code Signing Certificates and SSL Certificates are both digital certificates that use public key encryption, but that’s about where the similarities end. The underlying technical difference between a code signing certificate and a ssl certificate is small, but they’re security solutions for very different purposes.
Let’s look at the difference between Comodo Code Signing Certificates and Comodo SSL Certificates.
An SSL certificate is a piece of software that enables HTTPS on a website through the use of public key encryption. This enables the Secure label and padlock in your browser:
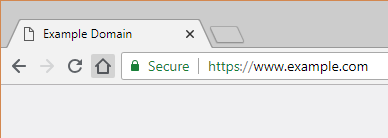
The SSL certificate authenticates the server to web browsers and facilitates a secured connection by encrypting communication between the website and its users. All modern SSL Certificates offer the same level of encryption, but they differ in terms of the authentication offered.
Bottom line: SSL certificates enable HTTPS to secure the communication to and from websites.
![]()
Need to enable HTTPS on your website? You can typically save a significant amount by buying your SSL certificate direct instead of through your web hosting company. We sell all Comodo SSL certificates at up to 75% off.
Compare SSL Certificates
A Code Signing Certificate authenticates the identity of a software developer or publisher and provides assurance that the signed piece of software has not been altered or tampered with. This is done by applying a digital signature and hashing it along with the software itself.
When a user attempts to download a piece of unsigned software the browser or antivirus program they’re running will flag it and insert a warning about it originating from an “unknown source” like this:
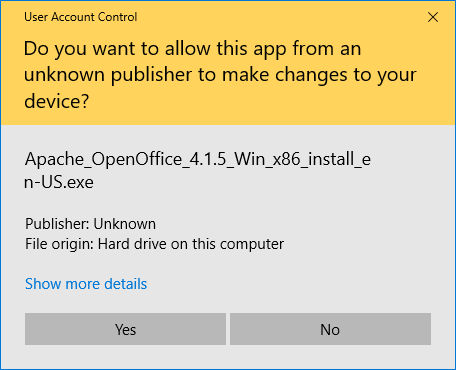
Code signing certificates help software developers avoid security warnings like this.
However, if the software is signed using a Comodo Code Signing certificate, the browser will trust the download and let it proceed. The browser will also be able to perform a check in the background that verifies the integrity of the signed code download.
There is also an Extended Validation version of Comodo Code Signing certificates, it helps developers by providing them with a substantial Microsoft Authenticode reputation boost with the Microsoft SmartScreen filter. The private key for these certificates also comes stored on an external hardware token for greater security.
Best of all, Comodo is one of the few CAs that offers Code Signing for individual developers, too. So whether you’re part of a team or doing it on your own, Comodo has a Code Signing certificate for you.

Need to sign your software to assure users and make installation easier? We sell all Comodo code signing certificates at up to 42% off.
View Code Signing Certificates
No. Although both are digital certificates, they are validated differently and have different enhanced key usages listed in the certificate. Trying to use one instead of the other will result in errors.
There’s an important different between code signing and ssl when it comes to expiration dates, also. If your website has an expired SSL certificate, it will trigger scary warnings to your user.
If a software executable was signed with a code signing certificate that is now invalid, no errors will display as long as the code signing certificate was valid when the code was signed and timestamped.
If you’re comparing code signing certificates vs ssl certificates, here’s the basic difference:
Another key difference is that SSL/TLS encrypts all communication between clients and servers, Code Signing doesn’t actually encrypt the software– it encrypts the signature and timestamp as part of the signature block. The actually integrity test is done via hashing.
Either way, if you needed to sum code signing certificate vs SSL certificate differences up in a sentence it would be: SSL encrypts websites, Code Signing protects software.