Rate this article: 


 (14 votes, average: 3.00)
(14 votes, average: 3.00)



 (14 votes, average: 3.00)
(14 votes, average: 3.00)Let’s talk about certificate chaining. The way trust works with relation to SSL is that the browsers are pretty much hard-coded to trust a handful of root certificates. The trusted roots come pre-installed in browsers’ trust stores. A trust store is a carefully curated collection of Roots that all of the trusted Certificate Authorities issue from. In order for an end user SSL certificate to be trusted, it has to chain back to one of those trusted roots. If it doesn’t the browser will issue a warning about the certificate in question.
When Comodo CA issues an SSL certificate, it will send along a specific Comodo CA bundle of intermediate certificates to install alongside it. These certificates create what is called a certificate chain. The end user certificate was signed using one of the intermediates, which was signed using one of the roots. When a browser arrives at a website it will attempt to build the certificate chain and chain the SSL certificate it’s being presented with back to one of the roots in its trust store.
You can easily view the certificate chain a website is using. Just click to view the certificate details:
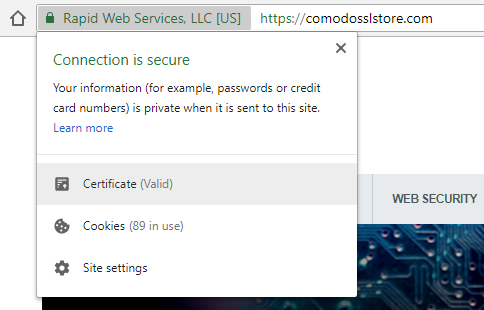
The click to view the certification path, which is the same as the certificate bundle / chain.
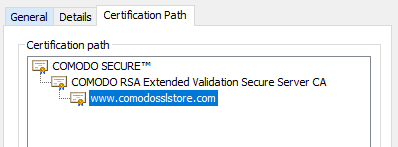
This screenshot shows a typical Comodo certificate chain – the site’s certificate chains to the COMODO RSA Extended Validation Secure Server CA (the intermediate for EV certificates) which chains back to the Comodo root (COMODO SECURE).
If your browser can authenticate the certificate chain, the connection ensues as planned. If it can’t, it’s almost always as a result of an issue with an intermediate certificate (or else someone was messing with their root store and accidentally deleted a root). Some browsers cache intermediates so they can try to build the certificate chain themselves, others don’t. From the standpoint of a site owner, the best move is always to address the chaining issue by installing the proper intermediate. Simply go back to the email you received your SSL certificates in and install the intermediates that were included with it.
We recommend you contact Comodo regarding this issue. They can typically send you the correct intermediate certificate for your end user one. Failing that, you can also re-issue the certificate and Comodo will include the Comodo CA bundle with the intermediate(s) and your new certificate. You may also want to swap out your SSL certificate while you install the intermediates– just for the sake continuity.
As a site owner, that’s not your problem. Comodo is universally trusted by browsers so if someone is having an issue with a root it’s client-side. There are two ways a user can fix this issue. They can either head to the Comodo website and download the lost root– but that requires knowing which Root needs to be installed. The easier method would just be to wipe your settings, delete your browser and re-install it. You should be back to your default root store by then. Just don’t edit anymore.

Tip: You can typically save a significant amount by buying your SSL certificate direct instead of through your web hosting company. We sell all Comodo SSL certificates at up to 75% off.
Compare SSL Certificates